

In vivo monoclonal production is longer in time and generally more expensive. Request a quote for polyclonal antibody production here!
The dose of immunogen and its proper proportion and emulsification together with the adjuvant However, in express protocols, different adjuvants than those are used. The best known and most used adjuvant are FCA (Freund’s complete adjuvant) and FIA (Freund’s incomplete adjuvant). The choice of adjuvantĪdjuvants are substances that, when administered together with the antigen, accelerate, increase or prolong the immune response. In express protocols, different routes of administration are often used, depending on the day of injection. The effectiveness of the immune response depends on the distribution of the antigen to the lymphoid tissue. The administration route (intramuscular, intraperitoneal or subcutaneous injection) Whether the epitope is continuous or discontinuous.The more exposed they are, the more likely to be recognized. The area of the protein where antigenic determinants are and their conformation.The length and composition of the sequence.Some concepts to take into account when opting for an express protocol are followings: There are different algorithms that computer programs use when designing one or several antigenic peptides. These rapid protocols are based on the following: A thorough study of the antigenįirst, it is necessary to determine the best protein areas as antigenic determinants. However, there are in vivo protocols for obtaining good quality polyclonal antibodies in less time.Įxpress protocols allow obtaining polyclonal antibodies in just 45 days.

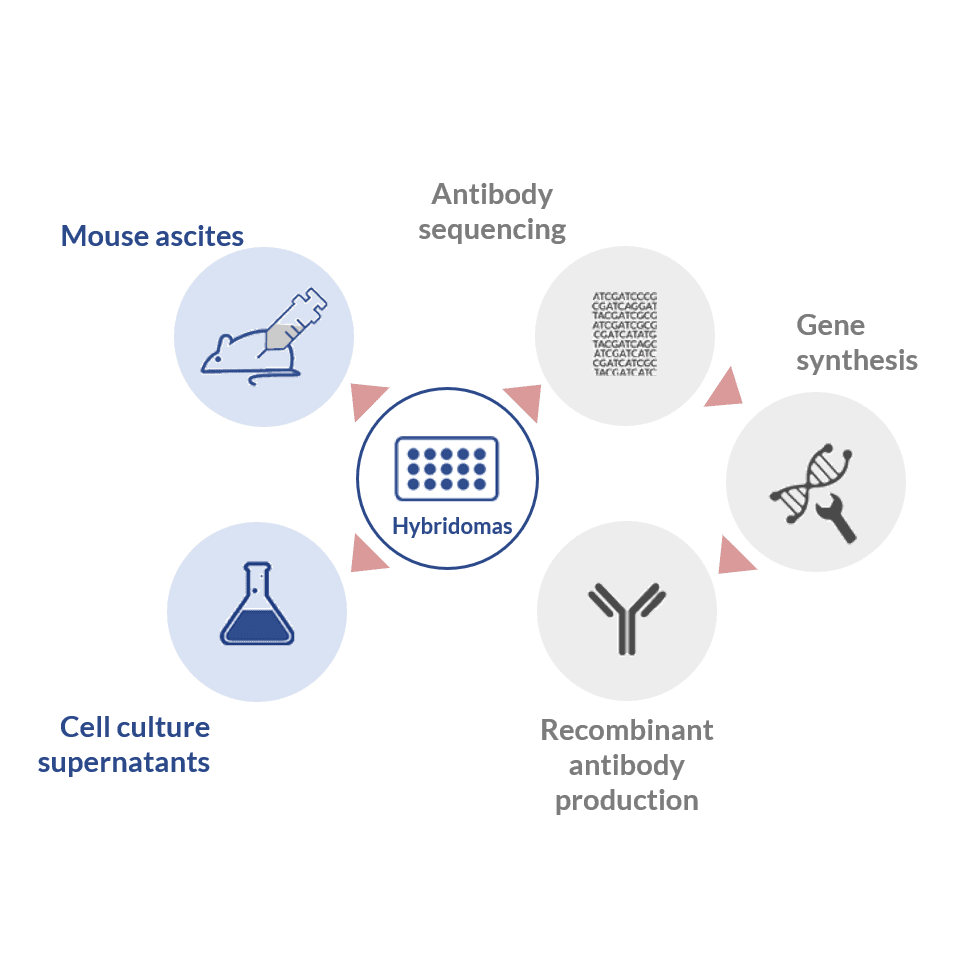
When the immunization period ends, the next step is the extraction and purification of the different antibodies that the animal has generated against the antigen used. During this period, the animal is immunized with an initial dose and several boosters. The production of polyclonal antibodies involves an in vivo process, and normally takes about 90 days. Our scientific team will assist you across all the process. We design and produce the reagent that best suits your research. However, there are alternatives that offer excellent results in a shorter period of time, such as express protocols or recombinant antibodies. The classic protocols for antibody production are usually long. The ability to generate this immune response, depends on the characteristics of the immunogen itself, the immunization protocol or the animal species selected. bioreactors or large flasks).Antibodies are classically obtained by stimulating the immune system of an animal using proteins or peptides as the immunogen. Expansion - Expand clones producing desired antibodies (e.g.Scale up and wean - Scale up clones producing desired antibodies and wean off selection agent(s).ELISA) each potentially high-producing colony. Functional characterization - Confirm, validate and characterize (e.g.Clone screening and picking - clones are screened and selected on the basis of antigen specificity and immunoglobulin class.Fusion - Myeloma cells and isolated splenocytes are fused together to form hybridomas in the presence of polyehthylene glycol(PEG), which causes cell membranes to fuse.Preparation of myeloma cells - Myeloma cells are immortalized cells that, once fused with spleen cells, can result in hybridoma capable of unlimited growth.The antibody-producing splenocytes are then isolated for in vitro hybridoma production. Immunization of mice & isolation of splenocytes - Mice are immunized with an antigen and later their blood is screened for antibody production.HIGH-THROUGHPUT, HIGH CONTENT SCREENINGĪ typical monoclonal antibody production process.PROTEIN DETECTION, QUANTITATION, ANALYSIS.NUCLEIC ACID (DNA/RNA) DETECTION & ANALYSIS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
